MBH-Seg: Multi-class Brain Hemorrhage Segmentation in Non-contrast CT
News
Check the leaderboard here:Leaderboard
[2024.11.8] The top-rank teams' presentations have been released. Please see thelink.
[2024.10.6] The final leaderboard has been released.
[2024.9.20] We are extending the second stage submission deadline by one week (September 28th, 2024).
[2024.9.13] Click Here to View theMBH-Seg@MICCAI2024 Programme
[2024.9.04] We have updated the instructions for the second stage evaluation.
[2024.8.19] The deadline for the 1st validation phase submission has been extended to September 6th, 2024.
[2024.7.29] We open the submission section for the 1st validation phase.
[2024.7.24] We are extending the submission deadline for the 1st validation phase by one week.
[2024.7.10] We add a new authentication method for participants registrations.
[2024.5.15] We opened the challenge website and released the training datasets.
Program

Overview
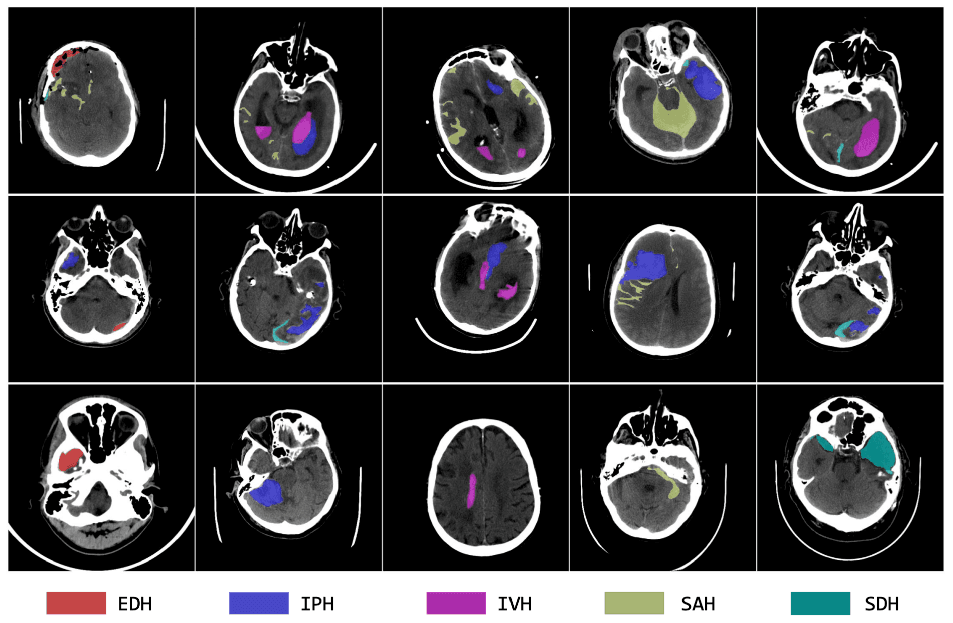
We invite you to participate in the first MBH-Seg Challenge. The focus of this year's challenge is to segment various types of brain hemorrhages base on non-contrast CT scans in a semi-supervised setting.Intracranial hemorrhage (ICH) encompasses bleeding within the skull or brain, manifesting in several types based on the anatomical location of the bleed relative to the brain and its surrounding membranes. These types include extradural hemorrhage (EDH), subdural hemorrhage (SDH), subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH), intraparenchymal hemorrhage (IPH), and intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH). The causes of ICH are varied, ranging from trauma and vascular malformations to hypertension and venous thrombosis. Detection and characterization of ICH are typically performed using non-contrast CT scans, which provide crucial insights into the type and distribution of the hemorrhage. Accurate localization, quantification, and classification of these hemorrhages are vital for clinical management, as they help clinicians assess severity, predict patient outcomes, and determine appropriate treatment strategies. Despite advances in deep learning that have propelled the automation of medical image segmentation, the segmentation of different ICH classes remains a challenge, particularly due to the scarcity of public datasets with multi-class, pixel-level annotations. Most existing datasets focus on hemorrhage classification or single-class segmentation (foreground vs. background), thus limiting the development of detailed segmentation tools.
This challenge enhances a public ICH dataset to create a comprehensive 3D, multi-class ICH dataset. This dataset will feature precise pixel-level hemorrhage annotations alongside a significantly larger pool of unannotated data. Participants are encouraged to employ semi-supervised learning techniques to develop diagnostic tools that are not only more consistent and rapid but also more accurate. Such advancements could potentially improve patient outcomes by reducing mortality and furthering the application of deep learning in medical imaging.
Prizes
1. Cash Awards:First Prize: $800
Second Prize: $400
Third Prize: $200
2. Certificates for the top-rank teams.
3. The top teams will be invited to give oral presentations at the MICCAI 2024 Event in person or virtually.
4. Co-author of the challenge paper, which will be submitted to a top journal (MedIA/TMI).
Schedule
| Event | Timeline | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Release of training data | May 15th, 2024 | ||||
| Submission for the 1st-Validation phase | From July 29th, 2024 to September 6th, 2024 (11:59pm UTC-11 Time) | ||||
| Announcement of attendance at the 2nd-Testing phase | September 7th, 2024 (11:59pm UTC-11 Time) | ||||
| Announcement of invited presentations | September 7th, 2024 (11:59pm UTC-11 Time) | ||||
| Submission for the 2nd-Testing phase | From September 7th, 2024 to September 28th, 2024 (11:59pm UTC-11 Time) | ||||
| Announcement of final leaderboards | September 29th, 2024 (11:59pm UTC-11 Time) | ||||
| Announcement of final invited presentations | September 29th, 2024 (11:59pm UTC-11 Time) | ||||
| The Challenge Day | October 6th, 2024 | ||||
Dataset
Acknowledgments and Citations
We express our gratitude for the significant contribution of the RSNA Intracranial Hemorrhage Detection Challenge Dataset.
1. Wu, Biao, Yutong Xie, Zeyu Zhang, Jinchao Ge, Kaspar Yaxley, Suzan Bahadir, Qi Wu, Yifan Liu, and Minh-Son To. "BHSD: A 3D Multi-class Brain Hemorrhage Segmentation Dataset." In International Workshop on Machine Learning in Medical Imaging, pp. 147-156. Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland, 2023.
2. AE Flanders, LM Prevedello, G Shih, et al. Construction of a Machine Learning Dataset through Collaboration: The RSNA 2019 Brain CT Hemorrhage Challenge. Radiology: Artificial Intelligence 2020;2:3.
3. Anouk Stein, MD, Carol Wu, Chris Carr, George Shih, Jayashree Kalpathy-Cramer, Julia Elliott, kalpathy, Luciano Prevedello, Marc Kohli, MD, Matt Lungren, Phil Culliton, Robyn Ball, Safwan Halabi MD. (2019). RSNA Intracranial Hemorrhage Detection. Kaggle. https://kaggle.com/competitions/rsna-intracranial-hemorrhage-detection
2. AE Flanders, LM Prevedello, G Shih, et al. Construction of a Machine Learning Dataset through Collaboration: The RSNA 2019 Brain CT Hemorrhage Challenge. Radiology: Artificial Intelligence 2020;2:3.
3. Anouk Stein, MD, Carol Wu, Chris Carr, George Shih, Jayashree Kalpathy-Cramer, Julia Elliott, kalpathy, Luciano Prevedello, Marc Kohli, MD, Matt Lungren, Phil Culliton, Robyn Ball, Safwan Halabi MD. (2019). RSNA Intracranial Hemorrhage Detection. Kaggle. https://kaggle.com/competitions/rsna-intracranial-hemorrhage-detection
Evaluation
Metric(s)
1. Dice Similarity Coefficient (Dice): Dice measures the overlap between the predicted segmentation and the ground truth at the pixel-level. It's highly relevant for medical image segmentation to ensure accurate delineation of affected areas.
2. Sensitivity: This metric assesses the class-level true positive rate, which refers to the test's ability to correctly detect ill patients out of those who do have the condition.
3. Specificity: This metric assesses the class-level true negative rate, which refers to the test's ability to correctly reject healthy patients without a condition.
For the final ranking, metrics will be aggregated for the Challenge Score (CS) as:
CS = 0.5 * Dice + 0.25 * Sensitivity + 0.25 * Specificity
Submission
Terms and Conditions
1. Only automatic methods are allowed
2. No private additional data is allowed. We will require all participants to provide extensive documentation on their development processes, including data and methods used. Top-ranked participants must submit their training code and checkpoints for verification. Publicly available pre-trained models are allowed, ensuring a level playing field and transparency in the competition's evaluation process.
3. Independent Publications: Participating teams are allowed to publish their results separately. However, this should be done in a manner that respects the collective efforts of the challenge.
4. Embargo Period: An embargo period allows the challenge organizers to publish a comprehensive challenge paper first. During this period, individual teams are encouraged to refrain from publishing their complete findings independently.
2. No private additional data is allowed. We will require all participants to provide extensive documentation on their development processes, including data and methods used. Top-ranked participants must submit their training code and checkpoints for verification. Publicly available pre-trained models are allowed, ensuring a level playing field and transparency in the competition's evaluation process.
3. Independent Publications: Participating teams are allowed to publish their results separately. However, this should be done in a manner that respects the collective efforts of the challenge.
4. Embargo Period: An embargo period allows the challenge organizers to publish a comprehensive challenge paper first. During this period, individual teams are encouraged to refrain from publishing their complete findings independently.
Community
Organizers
•Yutong Xie, Researcher, Australian Institute for Machine Learning (AIML), University of Adelaide, Australia
•Minh-Son To, Medical Practitioner, Flinders Health and Medical Research Institute, Flinders University, Australia
•Chenyu Wang, Senior Lecturer, Brain and Mind Centre, University of Sydney, Australia
•Dongang Wang, Researcher, University of Sydney, Australia
•Zhibin Liao, Researcher, Australian Institute for Machine Learning (AIML), University of Adelaide, Australia
•Yuankai Qi, Assistant Professor, Macquarie University, Australia
Advisor
•Qi Wu, Assoiate Professor, Australian Institute for Machine Learning (AIML), University of Adelaide, Australia
•Johan Verjans, Clinician-scientist, Royal Adelaide Hospital; Associate Professor, Australian Institute for Machine Learning (AIML), University of Adelaide, Australia
•Yong Xia, Professor, Northwestern Polytechnical University, China
Contributors
•Biao Wu, Student, University of Adelaide, Australia•Siqi Chen, Research Assistant, Australian Institute for Machine Learning (AIML), University of Adelaide, Australia
•Townim Faisal Chowdhury, PhD Student, Australian Institute for Machine Learning (AIML), University of Adelaide, Australia
•Vu Minh Hieu Phan, Researcher, Australian Institute for Machine Learning (AIML), University of Adelaide, Australia
•Yifan Liu, Lecturer, Australian Institute for Machine Learning (AIML), University of Adelaide, Australia
•An Thien An Hong, Resident Medical Officer, Royal Prince Alfred Hospital, Australia
Organized By






Contact Us
Please contact us if you have any enquires through our Google Form